Catégorie : Général
Ticagrelor versus clopidogrel in elective percutaneous coronary intervention (ALPHEUS): a randomised, open-label, phase 3b trial
Summary
Background
Percutaneous coronary intervention (PCI)-related myonecrosis is frequent and can affect the long-term prognosis of patients. To our knowledge, ticagrelor has not been evaluated in elective PCI and could reduce periprocedural ischaemic complications compared with clopidogrel, the currently recommended treatment. The aim of the ALPHEUS study was to examine if ticagrelor was superior to clopidogrel in reducing periprocedural myocardial necrosis in stable coronary patients undergoing high-risk elective PCI.
Methods
The ALPHEUS study, a phase 3b, randomised, open-label trial, was done at 49 hospitals in France and Czech Republic. Patients with stable coronary artery disease were eligible for the study if they had an indication for PCI and at least one high-risk characteristic. Eligible patients were randomly assigned (1:1) to either ticagrelor (180 mg loading dose, 90 mg twice daily thereafter for 30 days) or clopidogrel (300–600 mg loading dose, 75 mg daily thereafter for 30 days) by use of an interactive web response system, and stratified by centre. The primary outcome was a composite of PCI-related type 4 (a or b) myocardial infarction or major myocardial injury and the primary safety outcome was major bleeding, both of which were evaluated within 48 h of PCI (or at hospital discharge if earlier). The primary analysis was based on all events that occurred in the intention-to-treat population. The trial was registered with ClinicalTrials.gov, NCT02617290.
Findings
Between Jan 9, 2017, and May 28, 2020, 1910 patients were randomly assigned at 49 sites, 956 to the ticagrelor group and 954 to the clopidogrel group. 15 patients were excluded from the ticagrelor group and 12 from the clopidogrel group. At 48 h, the primary outcome was observed in 334 (35%) of 941 patients in the ticagrelor group and 341 (36%) of 942 patients in the clopidogrel group (odds ratio [OR] 0·97, 95% CI 0·80–1·17; p=0·75). The primary safety outcome did not differ between the two groups, but minor bleeding events were more frequently observed with ticagrelor than clopidogrel at 30 days (105 [11%] of 941 patients in the ticagrelor group vs 71 [8%] of 942 patients in the clopidogrel group; OR 1·54, 95% CI 1·12–2·11; p=0·0070).
Interpretation
Ticagrelor was not superior to clopidogrel in reducing periprocedural myocardial necrosis after elective PCI and did not cause an increase in major bleeding, but did increase the rate of minor bleeding at 30 days. These results support the use of clopidogrel as the standard of care for elective PCI.
High-dose influenza vaccine to reduce clinical outcomes in high risk cardiovascular patients: Rationale and design of the INVESTED trial
Effects of n-3 Fatty Acid Supplements in Elderly Patients after Myocardial Infarction: A Randomized Controlled Trial
Abstract
Background
High intake of marine n-3 polyunsaturated fatty acids (PUFA) has been associated with reduced risk of cardiovascular events; however, this has not been confirmed in patients with a recent acute myocardial infarction (AMI). Elderly patients are at particularly increased cardiovascular risk after MI, but few trials address this group specifically. Omega-3 fatty acids hold the potential to reduce cardiovascular events with limited adverse effects in this vulnerable group. The hypothesis was that daily addition of 1.8g n-3 PUFA to standard of care secondary prophylaxis in elderly patients who have survived an AMI would reduce the risk of subsequent cardiovascular events during 2 years follow-up.
Methods
The OMega-3 fatty acids in Elderly with Myocardial Infarction (OMEMI) trial is an investigator-initiated, multi-center, randomized clinical trial adding 1.8 g n-3 PUFA (930 mg EPA and 660 mg DHA) versus placebo (corn oil) daily to standard of care in 70-82 years old patients with recent (2-8 weeks) AMI. The primary endpoint was a composite of non-fatal AMI, unscheduled revascularization, stroke, all-cause death, heart failure hospitalization after two years. The secondary outcome was new atrial fibrillation. The safety outcome was major bleeding. Serum fatty acids were measured as biomarkers of adherence.
Results
In total, 1,027 patients were randomized. Follow-up data were available for 1,014 patients who were included in the intention-to-treat analysis. Mean ± SD age was 75±3.6 years, 294 (29%) were female and mean triglycerides were 111.4±61.9 mg/dL. The primary endpoint occurred in 108 (21.4%) patients on n-3 PUFA vs 102 (20.0%) on placebo (HR 1.08 [95%CI 0.82-1.41], p=0.60). The secondary endpoint occurred in 28 (7.2%) patients on n-3 PUFA vs 15 (4.0%) on placebo (1.84 [0.98 -3.45], p=0.06). Median changes in EPA and DHA were +87% and +16% for n-3 PUFA vs -13% and -8% for placebo. Major bleeding occurred in 54 (10.7%) and 56 (11.0%) in the n-3 PUFA and placebo groups, respectively (p=0.87). Similar results were found in per-protocol analysis (n=893).
Conclusions
We could not detect reduction in clinical events in our elderly patients with a recent AMI, treated with 1.8 g n-3 PUFAs daily for 2 years.
Rivaroxaban in Patients with Atrial Fibrillation and a Bioprosthetic Mitral Valve
Abstract
Background
The effects of rivaroxaban in patients with atrial fibrillation and a bioprosthetic mitral valve remain uncertain.
Methods
In this randomized trial, we compared rivaroxaban (20 mg once daily) with dose- adjusted warfarin (target international normalized ratio, 2.0 to 3.0) in patients with atrial fibrillation and a bioprosthetic mitral valve. The primary outcome was a composite of death, major cardiovascular events (stroke, transient ischemic attack, systemic embolism, valve thrombosis, or hospitalization for heart failure), or ma- jor bleeding at 12 months.
Results
A total of 1005 patients were enrolled at 49 sites in Brazil. A primary-outcome event occurred at a mean of 347.5 days in the rivaroxaban group and 340.1 days in the warfarin group (difference calculated as restricted mean survival time, 7.4 days; 95% confidence interval [CI], −1.4 to 16.3; P<0.001 for noninferiority). Death from cardiovascular causes or thromboembolic events occurred in 17 patients (3.4%) in the rivaroxaban group and in 26 (5.1%) in the warfarin group (hazard ratio, 0.65; 95% CI, 0.35 to 1.20). The incidence of stroke was 0.6% in the rivaroxaban group and 2.4% in the warfarin group (hazard ratio, 0.25; 95% CI, 0.07 to 0.88). Major bleeding occurred in 7 patients (1.4%) in the rivaroxaban group and in 13 (2.6%) in the warfarin group (hazard ratio, 0.54; 95% CI, 0.21 to 1.35). The frequency of other serious adverse events was similar in the two groups.
Conclusions
In patients with atrial fibrillation and a bioprosthetic mitral valve, rivaroxaban was noninferior to warfarin with respect to the mean time until the primary outcome of death, major cardiovascular events, or major bleeding at 12 months. (Funded by PROADI-SUS and Bayer; RIVER ClinicalTrials.gov number, NCT02303795.)
Assessment of Omega-3 Carboxylic Acids in Statin Treated Patients with High Levels of Triglycerides and Low Levels of High Density Lipoprotein Cholesterol: Rationale and Design of the STRENGTH Trial
Thrombophylaxie pharmacologique chez les patients COVID-19
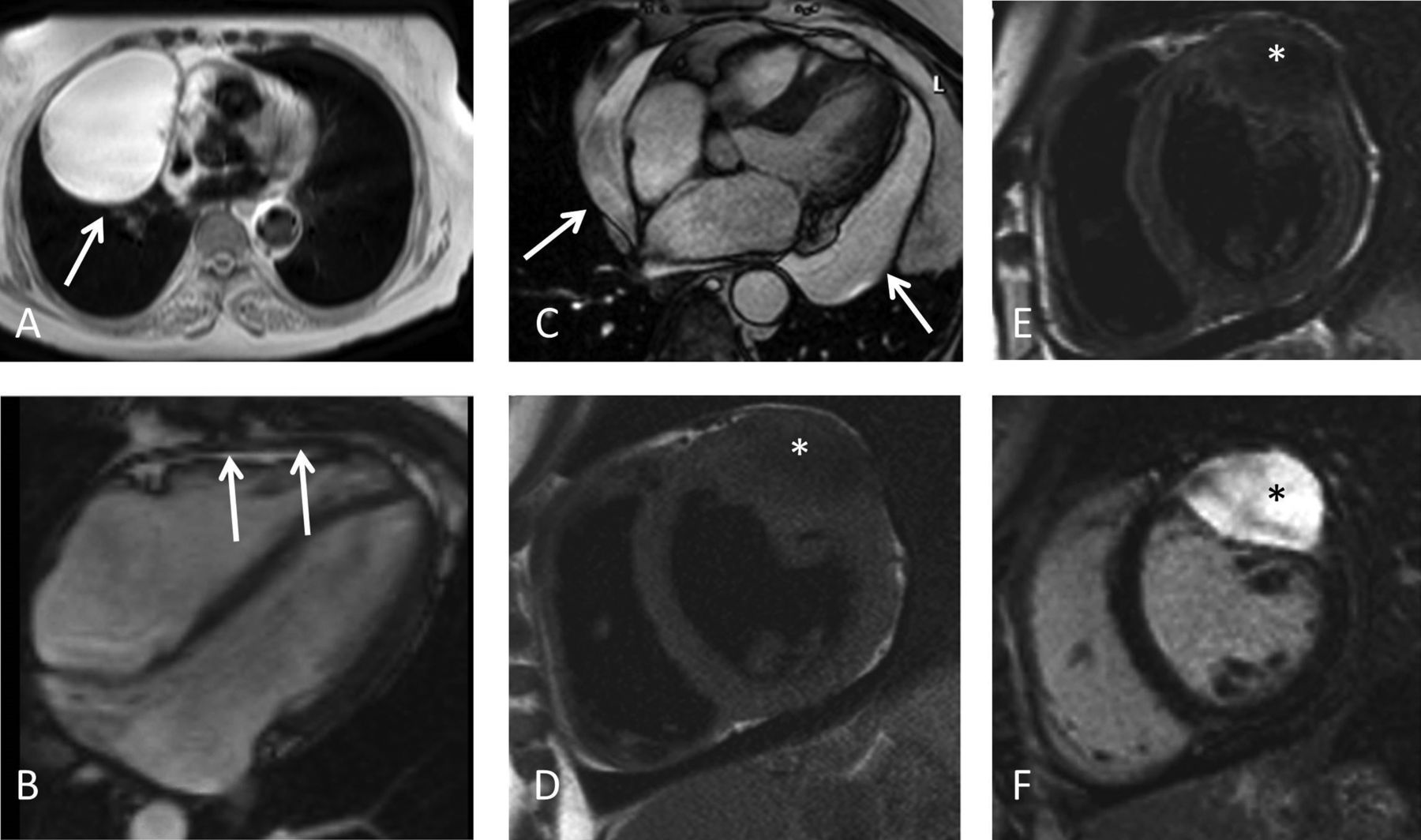
SCMR Position Paper (2020) on clinical indications for cardiovascular magnetic resonance
Abstract :
The Society for Cardiovascular Magnetic Resonance (SCMR) last published its comprehensive expert panel report of clinical indications for CMR in 2004. This new Consensus Panel report brings those indications up to date for 2020 and includes the very substantial increase in scanning techniques, clinical applicability and adoption of CMR worldwide. We have used a nearly identical grading system for indications as in 2004 to ensure comparability with the previous report but have added the presence of randomized controlled trials as evidence for level 1 indications. In addition to the text, tables of the consensus indication levels are included for rapid assimilation and illustrative figures of some key techniques are provided.
Clinical Trials for Vascular Complications of COVID-19: An Overview
Connie N. Hess, MD, MHS University of Colorado School of Medicine CPC Clinical Research
Rationale and design of the AFFIRM-AHF trial: a randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial comparing the effect of intravenous ferric carboxymaltose on hospitalisations and mortality in iron-deficient patients admitted for acute heart failure
Aims
Iron deficiency (ID) is a common co-morbidity in heart failure (HF), associated with impaired functional capacity, poor quality of life and increased morbidity and mortality. Treatment with intravenous (i.v.) ferric carboxymaltose (FCM) has shown improvements in functional capacity, symptoms and quality of life in stable HF patients with reduced ejection fraction. The effect of i.v. iron supplementation on morbidity and mortality in patients hospitalised for acute HF (AHF) and who have ID has yet to be established. The objective of the present article is to present the rationale and design of the AFFIRM-AHF trial (ClinicalTrials.gov NCT02937454) which will investigate the effect of i.v. FCM (vs. placebo) on recurrent HF hospitalisations and cardiovascular (CV) mortality in iron-deficient patients hospitalised for AHF.
Methods
Iron deficiency (ID) is a common co-morbidity in heart failure (HF), associated with impaired functional capacity, poor quality of life and increased morbidity and mortality. Treatment with intravenous (i.v.) ferric carboxymaltose (FCM) has shown improvements in functional capacity, symptoms and quality of life in stable HF patients with reduced ejection fraction. The effect of i.v. iron supplementation on morbidity and mortality in patients hospitalised for acute HF (AHF) and who have ID has yet to be established. The objective of the present article is to present the rationale and design of the AFFIRM-AHF trial (ClinicalTrials.gov NCT02937454) which will investigate the effect of i.v. FCM (vs. placebo) on recurrent HF hospitalisations and cardiovascular (CV) mortality in iron-deficient patients hospitalised for AHF.
Conclusions
The AFFIRM-AHF trial will evaluate, compared to placebo, the effect of i.v. FCM on morbidity and mortality in iron-deficient patients hospitalised for AHF.